


🚩 Citizen Charter: What It Means for You
Imagine walking into a government office, knowing exactly what to expect—the documents you’ll need, the time it should take, and how to lodge a complaint if things go wrong. That’s the promise of a Citizen Charter—a friendly agreement between you and public institutions. In this conversational, SEO‑optimized guide (complete with real‑life stories and FAQs), we’ll break down what Citizen Charters are, why they matter, and how they really work for people across India 🇮🇳.
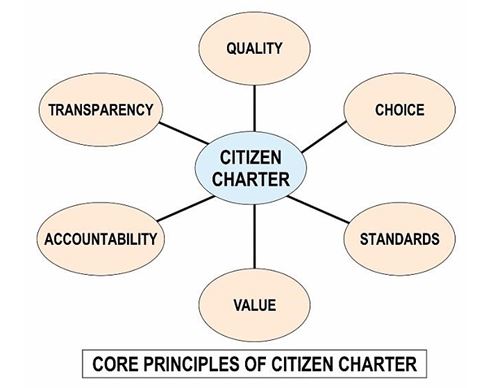
1. What Is a Citizen Charter? 🤝
At its heart, a Citizen Charter is a public commitment. Think of it as a memorandum of understanding between government bodies and you—the citizens.
- It spells out the standards of service, i.e., what public bodies promise to deliver (say, passport issuance within 30 days).
- It outlines time-bound delivery, such as processing building permits in 10 business days.
- It explains grievance redressal mechanisms, so you know how to lodge and escalate complaints.
- It also states your responsibilities—for instance, that you must provide accurate documents and pay fees. These charters are voluntary—not legally binding. Unlike rights under RTI or anti-corruption laws, these are more like a service contract, not enforceable in court.
2. How Did We Get Here?
- The concept originated in the UK in 1991, aiming to improve government responsiveness.
- In May 1997, Indian Chief Ministers created a roadmap for Citizen Charters, and the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) coordinated their rollout. By 2005, over 700 charters were implemented across central and state bodies. Despite efforts to make them legally enforceable (including a draft 2011 bill), Citizen Charters remain non‑binding. They rely on administrative goodwill and public pressure.
3. Why Should You Care?
- Transparency: You get clear information on fees, processing times, and required documents.
- Accountability: Officials are expected to meet standards—failing which you can challenge them.
- Grievance handling: A citizen charter forces an agency to equip itself with a complaint mechanism.
- Efficiency & trust: Set standards help reduce red tapism, build trust, and even curb petty corruption. For example, Indian Railways’ Passenger Charter promises cleaner coaches and on‑time departures; Hyderabad’s water board pledges compensation if services fail—thanks to their charters
4. Key Components of a Charter
According to governance guidelines, a robust charter should include:
- Vision & mission of the organization
- Services offered, with service standards
- Required documents and fees
- Delivery timelines
- Grievance redressal steps and responsible officers
- Accessibility provisions for disabled or marginalized groups
- Citizen responsibilities (e.g. honesty, punctuality)
- Review & feedback mechanisms to fine-tune services
5. Real-Life Stories: When Charter Meets Reality
🏙️ Story A: Clean Coaches, Happy Travelers
Railway passengers used to nag daily about dirty coaches. After the Passenger Charter was announced, travelers began pushing for accountability. Results? Cleaner coaches, prompt redressal, and passenger satisfaction surged.
🚰 Story B: Hyderabad’s Compensation Commitment
A local water consumer group fired up when water delivery faltered frequently. Referencing the water board’s Citizen Charter, they demanded compensation. The board complied—marking real accountability in public service delivery.
🏛️ Story C: Chandigarh’s Encroachment Mess
A Chandigarh resident, Amitpal Sharma, filed a charter-based complaint about street encroachments. The municipal corporation had 3 days to respond—the result? Silence. Despite repeated follow-ups, nothing changed. This echoes what research shows: implementation often falls flat.
6. Frequent Roadblocks
Despite the promise, most charters underwhelm due to:
- No legal teeth—failures carry no penalties.
- Poor awareness—many citizens don’t even know they exist.
- Weak content—commitments often vague or unrealistic.
- No enforcement—officials ignore charters as extra paperwork.
- Outdated updates—charters gather dust post-launch.
- Design failure—charters often drafted without citizen input.
7. Making Charters Work Better
Want charters that actually work? Here’s how:
- Set clear, measurable standards—e.g., “land records issued in 10 days.”
- Involve citizens in design—let actual users help define the charter.
- Launch public awareness—use social media, newspapers, even village meetings to inform citizens.
- Train staff—grow capacity for charter awareness and grievance handling.
- Monitor & review—use citizen feedback and surveys; update charters annually.
- Connect charters to rewards & penalties—recognize compliance and act on violations.
- Link with RTI & social audits—23 states have Right‑to‑Service laws; charters can complement these, RTI helps track violations, and social audits add public oversight.
8. FAQs: Your Charter Questions—Answered!
Q1: Are Citizen Charters legally binding?
No. They’re commitments to best practice, not enforceable laws. But public pressure can make them work.
Q2: Who issues a Citizen Charter?
Any government agency—central, state, or local—can create one under DARPG guidelines. Over 700 have been adopted.
Q3: What if officials don’t follow their charter?
You can file complaints through their grievance mechanisms, RTI applications to access service performance data, or approach Lokpal/Lokayukta if corruption is suspected. Social audits add public scrutiny.
Q4: Can poor or illiterate people use these?
Yes—charters must detail accessible complaint procedures. Awareness campaigns help marginalized groups. Still, implementation gaps persist and require bridging.
Q5: How are charters updated?
Ideally, annually—based on feedback. But many charters go unmodified for years, losing relevance.
9. The Bigger Picture: Citizen Charter and Governance
Citizen Charters are part of Sevottam, the Indian excellence framework for public service delivery:
- Includes charters & standards
- Grievance redressal systems
- Citizen feedback & continuous improvement loops
Together with:
- RTI laws for transparency
- Right-to-Service Acts in 22 states for guaranteed timelines
- Social audits under NREGA for public monitoring
These tools create a web of accountability. But a charter by itself needs your voice to turn words into action.
10. Your Action Plan: How to Use Citizen Charters
- Search the charter online for the department you need.
- Review the service standards and timelines.
- Engage in service confidently—know your rights and duties.
- Note delays or failures—record dates and officials.
- Lodge complaints formally, citing the charter section.
- Use RTI to inquire about missed standards if there’s no response.
- Get social—raise the issue with activists, community forums, or social audit bodies.
- Expand—push your local body to revise and publicize their charter.
11. Wrapping Up
Citizen Charters are a powerful yet underused tool for legal awareness and accountability in India. They reflect what should happen in public service, even if they don’t guarantee it. But with awareness, collective action, and smart use of other governance tools, citizens can make these charters more than just words.
Stand up. Speak out. Let the charter work for you—and inspire others to do the same.



🛠️ Grievance Redressal Mechanisms in Indian Government Offices: Your Rights, Your Voice 🇮🇳
When a public service fails us—be it a delayed pension, a broken road, or unresponsive officials—we often feel powerless. But India has built a robust web of grievance redressal channels designed to hold government accountable and fix issues. In this conversational guide, we’ll explore:
- ⚙️ Types of grievance mechanisms
- 📝 Step‑by‑step process for filing complaints
- ✅ Real-life case studies
- 🤔 Common FAQs
- 🛡️ Tips for making your complaint count
By the end, you’ll not only know how to complain—you’ll know where and why it truly matters. Let’s go!
1. Overview: What Channels Are Open to You?
India’s grievance ecosystem covers multiple layers of government:
- CPGRAMS / PG Portal (Centralized): Handles grievances against central and state departments
- State & CM Helplines: Offices of Chief Ministers/District Magistrates often run public grievance cells with helplines, complaint boxes, and WhatsApp options
- Vigilance/ACBs: For corruption allegations (e.g. Haryana ACB’s hotline, website) .
- Sector‑specific portals: Like E-Nivaran (Income Tax), Mera Aspataal (hospitals), Railways’ Nivaran .
- Lok Adalat / Consumer Forums: For disputes with public authorities or public utilities.
- Right-to-Service Acts (RTS): Enacted by 22 states to enforce guaranteed service timelines and penalties.
2. The Primary Route: CPGRAMS
What is CPGRAMS?
The Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System is the go-to online portal for citizen complaints—available 24×7, integrated with UMANG, and backed by a mobile app.
Key Features:
- Single portal, multiple wings: 92 central ministries and 36 states/UTs participate.
- Quick resolution norm: Grievances should be closed within 30 days, recently reduced to 21 days by DARPG.
- AI-assisted monitoring through a Grievance Redressal Assessment Index (GRAI) and “Next‑Gen CPGRAMS”.
- Feedback and Appeals: Closed cases prompt citizen feedback; unhappy with the resolution? File an appeal via the portal.
How to File:
- Register on CPGRAMS/UMANG app.
- Lodge a grievance: department, issue, dates, supporting docs.
- Get a Registration ID: for tracking.
- Track regularly; if delayed, ask for updates or interim replies.
Senior Officer Oversight:
Now, senior-level reviews are routine—similar to PMO review, with nodal officers ensuring timely resolution.
3. Local & State-Level Options
Besides CPGRAMS:
- CM/DM Offices: E.g., Delhi installs complaint boxes and WhatsApp lines monitored by CM’s office.
- Public Hearings: Several states (like Odisha) hold grievance camps where ministers/directors meet citizens directly.
- Vigilance/ACB: Best for anti-corruption cases; your identity is protected .
- Sector Portals: Direct redressal for grievances like hospital care or tax refunds .
4. Real-Life Wins: Proof It Works
✅ Bengaluru’s Unpaved Road
A student filed a CPGRAMS grievance about dust from a damaged road. A month later, the road was under repair—and photos confirmed the fix.
“I filed a grievance…to NHAI…within a month…work had begun.”
“Encourage everyone to use CPGRAMS to resolve civic issues.”
📈 GST Registration Fix
Rajesh Choudhary’s delayed GST registration was escalated via CPGRAMS and resolved quickly, enabling him to run his business smoothly.
🏫 School or PGRS Camps
In Andhra Pradesh’s Manyam district, 203 grievances—from pensions to electricity—were addressed swiftly during weekly grievance camps at the Collectorate.
These victories show that complaints—when used right—bring real change.
5. FAQs
Q1: Can I escalate if there’s no reply in 30 days?
Yes—CPGRAMS requires an interim response. With no full resolution, file an appeal online or escalate to the grievance officer.
Q2: What if the answer is unsatisfactory?
Give feedback as “Poor” on the portal, which unlocks appeal functionality. You can also file RTI, approach courts, talk to media, or use Lok Adalat for justice.
Q3: Is CPGRAMS the only portal?
No—you have CM/DM offices, Vigilance cells, sector-specific schemes, and even Lok Adalat for judicial redress. See section 1 for full list.
Q4: Digital access issues?
Yes, not everyone is digitally literate. Many states use offline camps, call centers, and boxes to bridge the gap. Rural outreach programs train citizens through CSCs and radio jingles .
Q5: What kind of grievances are excluded?
Matters under active court hearing, personal family issues, religious matters, and RTI-related requests are out of scope.
6. Tips to Make Your Complaint Count
- Be clear and specific: provide names, dates, department details.
- Upload evidence: photos, bills, documents—visible and legible.
- Follow timelines: check/respond within 21/30 days.
- Use feedback feature honestly: Poor rating triggers escalation.
- Escalate smartly: use appeals, RTI, or Lok Adalat if unresolved.
- Document everything: save IDs, screenshots, responses.
- Spread awareness: share your success—more users means stronger systems.
7. Why This Matters
- 💡 Empowerment: Citizens no longer suffer silently—you hold power.
- ⚖️ Transparency: Government becomes more open when complaints are visible.
- 🛑 Accountability: Officials are pushed to act, reducing delinquency.
- 🌐 Collective change: Many small fixes add up to systemic reform.
Darpg reports show CPGRAMS has redressed over 1.12 crore grievances, with average closure time ~15–18 days—proof that collective voice triggers governance change
8. The Road Ahead: What’s Changing?
- 21-day resolution window now enforced across central departments.
- PMO-style senior oversight ensures departments don’t ignore issues
- Tech upgrades: AI dashboards, multilingual apps, rural outreach drives .
- Citizen feedback focus: Call-center follow-ups and GRAI scorecards for agencies.
9. What You Can Do Now
- Find your grievance portal: CPGRAMS, CM helpline, or sector app.
- Draft your complaint: clear facts, attachments, and expectations.
- File & track it: note down your ID and monitor often.
- Use feedback & appeals: don’t settle for fair-sounding responses.
- Share your success: inspire others by telling your story.
- Keep pressure up: escalate if no action; involve oversight bodies or courts.
10. Closing Thoughts
Grievance redressal in India isn’t abstract—it delivers real fixes within weeks. We’ve seen roads repaired, government delays addressed, and clogged systems unclogged. But success relies on citizens who speak up.
Your complaint matters. Your voice drives change. And your story inspires a stronger democracy. The systems are there—use them. Let’s build accountable governance, one grievance at a time.
